Volumetric Analysis Numericals Problem Solution
Grade 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Volumetric Analysis Numericals Questions Answer Solution
Normality
Normality is defined as the no. of gram equivalent of solute present in one liter of the solution. It is represented as N.
$$No of gm eq = frac{Wt of Substance ( gm)}{Eq Wt}$$
| Compounds | Molecular wt. | Equivalent wt. | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | 36.5 | 36.5 | 1 |
| Sulphuric acid | 98 | 49 | 2 |
| Oxalic acid | 126 | 63 | 2 |
| Sodium hydroxide | 40 | 40 | 1 |
| Sodium carbonate | 106 | 53 | 2 |
| Calcium carbonate | 100 | 50 | 2 |
| Aluminium | 27 | 9 | 3 |
| Magnesium | 24 | 12 | 2 |
How many gram of sodium carbonate is required to prepare 250ml of decinormal solution of sodium carbonate?

Calculate the concentration of solution obtained by dissolving 0.63gm of oxalic acid into 200ml of solution.

Molarity
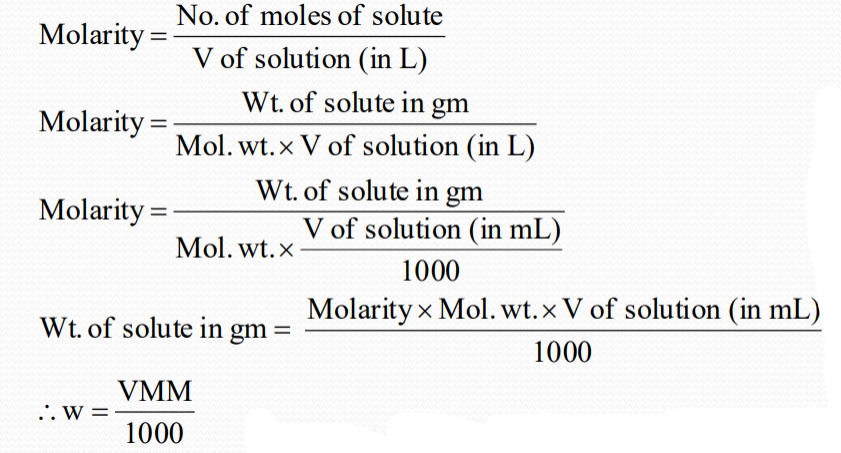
Gm/liter:
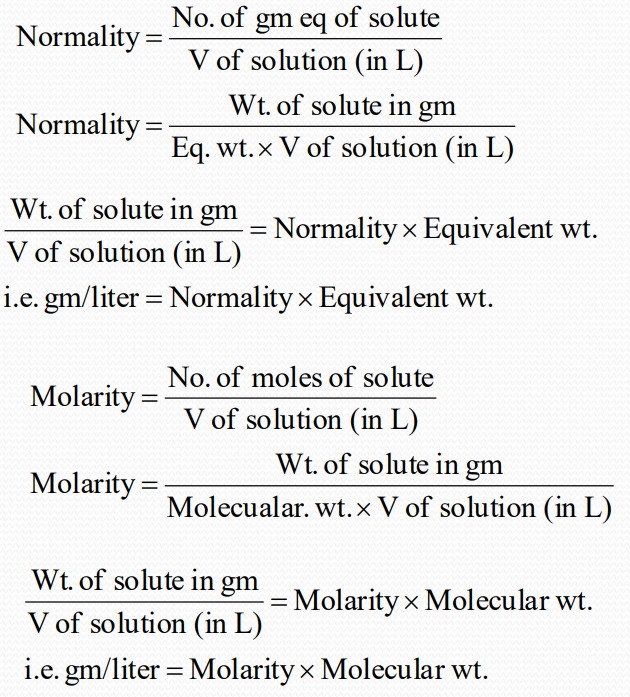
Relationship between normality and molarity:

Percentage (%)
100ml of solution is called percentage (by
volume).

Some Important Formula
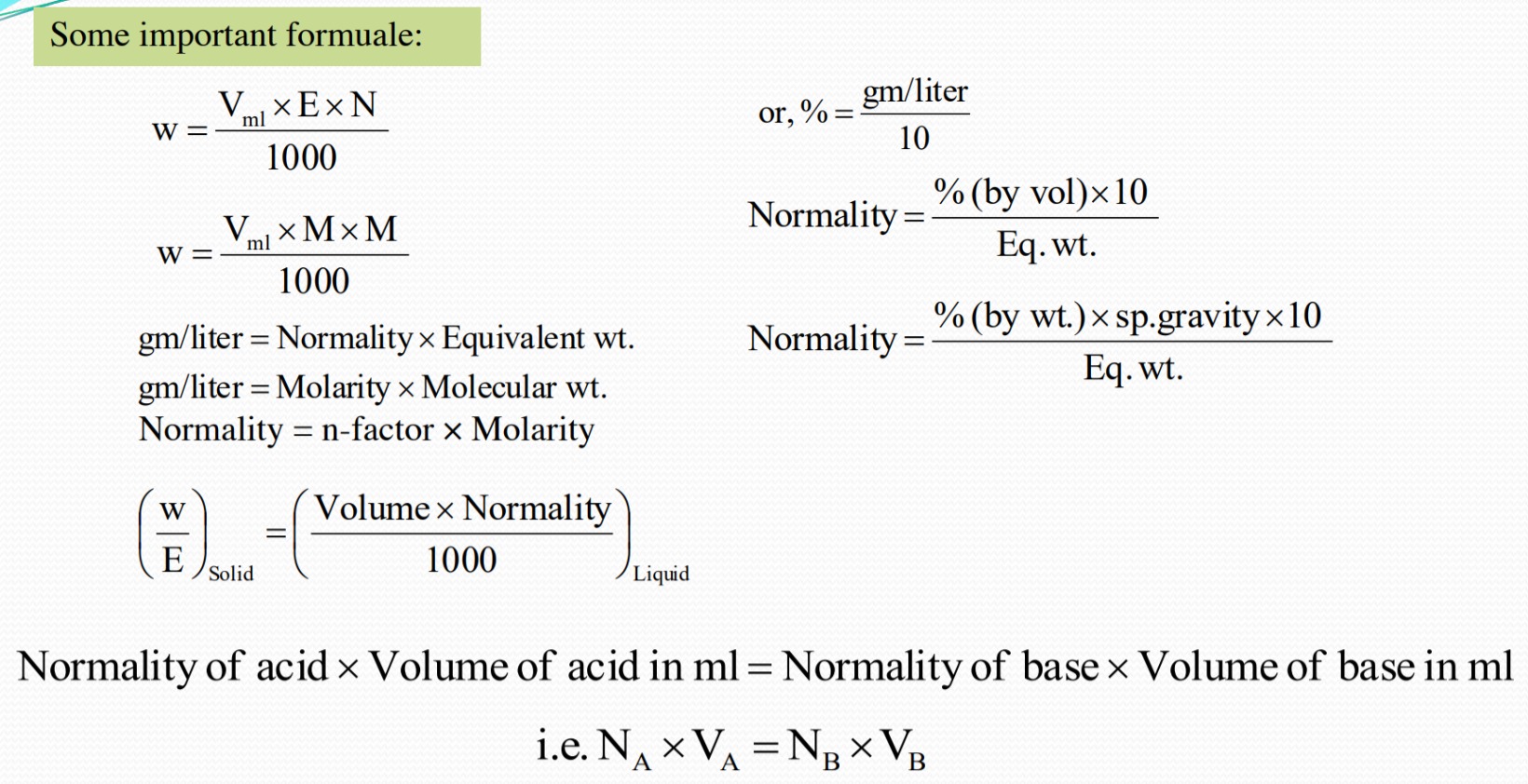
1) Express the following in g. eqvt. and moles
i) 1.06 g. Na 2 CO 3
We have, g. eqvt.
= $$frac{given wt}{eqvtwt} $$
= $$frac{1.06}{53} = 0.02$$
no. of moles
= $$frac{given wt}{eqvtwt} $$
= $$frac{1.06}{106} = 0.01$$
ii) 150 ml. of 0.1M NaOH solution
We have, g. eqvt. = normality x vol. in litre
= $$0.1*frac{150}{1000}$$ (in NaOH, N =M)
= 0.015
No. of moles = molarity x vol.in litre
= $$0.1*frac{150}{1000}$$
= 0.015
2) Calculate the wt. of anhydrous Na2CO3 required to prepare 250 ml. of $$frac{N}{20}(f = 1.01)$$ solution.
We have, $$X = frac{NEV}{1000}$$
$$= frac{1*1.01*53*250}{20*1000}$$
= 0.67 g
3) How many kg of wet NaOH containing 12% water are required to make 120 L of a 0.25 N solution.
We have,$$X = frac{NEV}{1000}$$
$$= frac{0.25*40*120*1000}{1000}$$
= 1200 g.=1.2 kg.
Let the wt. of wet NaOH be y g.
A/Q, (100-12) % of y = x
or, $$frac{88}{100}*y$$=1.2 kg.
or, y = 1.363 kg.
4) You are given a L of semi molar solution of oxalic acid. What volume of water should be added into it to make it exactly decinormal?
Here, V1 = 1L V2 = (1+x) L
S1 = $$frac{M}{2}$$ = 1N
S2 = $$frac{N}{10} $$= 0.1 N
(In oxalic acid, N = 2M)
We have, from normality equation:
V1 S1 = V2 S2
or, 1 * 1 = (1 + x) * $$frac{N}{10} $$
or, 1+ x =10
or, x = 9 L
5) Concentrated hydrochloric acid has a specific gravity of 1.16 & contains 32% HCl by wt. calculate the vol. of this acid which would be required to make 10 L of a normal solution of the acid.
a) Calculation of concentration of conc. HCl
We have, Normality $$= frac{% (frac{w}{w})*sp. gravity*10}{eqvt wtldotp }$$
$$= frac{32*1.16*10}{36.5}$$
= 10.17 N
b) Calculation of vol.
Here, V1 =? V 2 = 10 L
S1 = 10.17 N S2 = 1 N
We have, from normality equation:
$$V_1 S_1 = V_2 S_2$$
or, V 1 x 10.17 N = 10 x 1 N
V1= 0.983 L
6) x g. of oxalic acid reacts completely with 20 ml. of $$frac{N}{10}(f = 1.06)$$ $$ KMnO_4$$ solution. Calculate the value of x.
Here, g. eqvt. of oxalic acid = g. eqvt. of KMnO4
or, $$(frac{given wt.}{eq. wt})_$$Oxalic acid = ( normality*g. eqvt. of $$KMnO_4)$$
$$frac{X}{63} = 0.1*1.06*frac{20}{1000}$$
X = 63*0.1*1.06*0.02g.
X = 0.133g.
7) If 20 ml. of $$frac{N}{20}(f = 2.06)$$ $$H_2SO_4$$ and 30 ml.of $$frac{N}{10}(f = 1.12)$$ HNO 3 are mixed together, calculate the normality of mixture.
We have, $$V_m S_m = V_1 S_1 + V_2 S_2$$
or, (20 +30) * $$S_m$$ = 20 * 0.05 * 2.06 + 30 * 0.1 * 1.12
or, $$S_m$$ x 50 = 2.06 + 3.36
or, $$S_m$$ = 5.42/50
∴ $$S_m$$ = 0.1084 N
8) What volume of semi normal and centimolar $$H_2SO_4$$ solutions should be mixed in order to prepare 1.5 L of decinormal solution of $$H_2SO_4$$?
Let, $$V_1$$ = y $$V_2$$ = 1.5-y
$$S_1 = frac{N}{2}$$
$$S_2 = frac{M}{100} = frac{N}{50}$$
We have, $$V_m S_m = V_1 S_1 + V_2 S_2$$
or, $$1.5 * frac{N}{10} = y * frac{N}{2} + (1.5-y) * frac{N}{50}$$
or, 0.15 = 0.5y + 0.03 – 0.02y
or, 0.48y = 0.12
or, y = $$frac{0.12}{0.48}$$ = 0.25 L
Thus, the vol. of semi normal $$H_2SO_4 $$= y = 0.25 L
The vol. of centimolar $$H_2SO_4 $$ = 1.5-y = 1.5-0.25=1.25 L
9) 30 c.c. of 0.2N HCl, 10 c.c. of 1N $$H_2SO_4 $$, 20 c.c. of $$frac{N}{10}$$HNO3 and 40 c.c. of water are mixed together. What will be the normality of the mixture?
We have, $$V_m S_m = V_1 S_1 + V_2 S_2+V_3 S_3 + V_4 S_4$$
or, 100 x $$S_m$$ = 30 x 0.2 + 10 x 1 +20 x 0.1 + 40 x 0
or, 100 x $$S_m$$ = 6 + 10 + 2 + 0
or, $$S_m$$ = $$frac{18}{100}$$ = 0.18N
Read: Class 12 Chemistry Notes
Remaining Numericals









![NEB Class 12 Exam Routine 2081/2082 [2025]](https://iswori.com.np/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/neb-class-12-routine.png)