| Unit 8 | Haloalkanes class 12 |
| 8.1 | Nomenclature |
| 8.2 | Classification |
| 8.3 | Isomerism |
| 8.4 | Preparation (alkanes, alkenes, and alcohols) |
| 8.5 | Physical properties |
| 8.6 | Chemical properties (SN1 and SN2) |
| 8.7 | Formation (alcohol, nitrile, amine, ether, thioether, carbylamine, nitrite, and nitroalkane) |
| 8.8 | Elimination Reaction ( Saytzeff ’s rule) |
| 8.9 | Reaction with Sodium metal (Wurtz’s Reaction) |
| 8.10 | Reduction Reaction of Haloalkane |
| 8.11 | Preparation of Chloroform |
| 8.12 | Physical properties of Chloroform |
| 8.13 | Chemical properties of Chloroform |
%20Class%2012%20notes%20NEB%20Nepal.jpg) |
| Class 12 notes: Haloalkanes with important Questions |
Table of Contents
Unit 8: Haloalkane class 12
Introduction
Haloalkanes
are the derivatives of hydrocarbon because they are derived by replacing
hydrogen with halogen atoms, therefore the halogen derivatives of alkane are called
haloalkanes. Or
The organic compound containing halogen atom (X=-F,-Cl, -Br, -I) as a
functional group
is called Haloalkanes.
They are also called Alkyl halides.
Uses: Solvent, Medicine, Insecticide, etc.
Haloalkanes are formed by the replacement of one or more
hydrogen atoms
of alkane by the same number of halogen atoms and are bonded with the
carbon atom of alkane through a strong covalent bond. They are
presented by the general molecular formula
CnH2n+1X.
Nomenclature of haloalkanes
Prefix: side chain
branches substituents
Word root: number of C-atoms
Primary suffix: nature of C-atoms (-ane or -one or -one)
| Formula | Common name (Alkyl+halide) | IUPAC name (Halo +word) |
|---|---|---|
| R-X | alkyl halide | halo alkane |
| CH₃F | methyl fluoride | fluoro methane |
| CH₃CH₂-Cl | ethyl chloride | chloro ethane |
| CH₃CH₂CH₂Br | propyl bromide | 1-Bromo propane |
| CH₃CH₂-I | ethyl iodide | iodo ethane |
| CHCl₃ | chloroform | tri chloro methane |
| CHI₃ | iodoform | tri iodo methane |
| CCl₄ | carbon tetrachloride | tetra chloro methane |
| CH₃-CH-Cl₂ | ethylidene chloride (geminal dichloride) | 1,1-dichloro ethane |
| Cl-CH₂-CH₂-Cl | ethylene dichloride (Vicinal dichloride) | 1,2-dichloro ethane |
| CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl | n-propyl chloride | 1-Chloro propane |
| tertiary butyl bromide (Neo-butyl bromide) | 2-Bromo, 2-methyl propane |
| CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Br | n-butyl bromide | 1-Bromo butane |
| iso-butyl bromide | 1-Bromo-2-methyl propane |
| isopropyl chloride | 2-chloro propane |
| secondary butyl bromide | 2-Bromo butane |
Classification of haloalkanes
[A] Based on the nature of the carbon atom
1. Primary haloalkane (1 ̊)
The haloalkane in which the halogen-containing
carbon is further
bonded to one carbon atom (one alkyl group) or primary carbon is called
primary haloalkane.
| Primary haloalkane |
2. Secondary haloalkane (2 ̊)
The haloalkane in which the halogen-containing carbon is further bonded
to two carbon atoms (two alkyl groups) or secondary carbon is called
secondary haloalkane.
| Secondary Haloalkane |
3. Tertiary haloalkane (3 ̊)
The haloalkane in which the halogen-containing carbon is further bonded
to three carbon atoms (three alkyl groups) or tertiary carbon is called
tertiary haloalkane.
| Tertiary Haloalkane |
[B] based on the number of halogen atoms
Haloalkane contains only one halogen atom.
| Mono-haloalkane |
Haloalkane contains two halogen atoms.
| Di-haloalkane |
Haloalkane contains three or more halogen atoms.
| Poly-haloalkane |
Isomerism in haloalakanes
1. Chain isomerism
Haloalkanes have the same number of carbon atoms but the different
number in carbon chain length is called chain isomers.
| chain isomerism: Bromo pentane |
2. Position isomerism
Haloalkanes have the same molecular formula but different positions of halogen atoms
on the carbon chain are called position isomers.
| position isomerism: chloropropane |
Self-test:
Q.Write all possible isomers with the molecular formula C4H9I and give
their IUPAC name.
General methods of preparation of haloalkane
1. From alkanes (Halogenation of alkanes)
The haloalkanes are prepared by treating
alkane with a limited amount of halogen in presence of halogen carriers and sunlight or heat.
| Formation of haloalkane from an alkane |
On excess supply of chlorine poly-substituted product is formed.
| methane to tetra chloromethane in excess of chlorine |
In the case of higher alkanes two or more possible products are formed.
| higher alkanes give more than one products |
The bromination is carried out in presence of FeBr₃ under sunlight or heat.
The iodination of an
alkane
is a reversible reaction. So to obtain iodoalkane strong oxidizing agent like conc.HNO₃ or HIO₃ is used to increase the rate of the forward reaction.
 |
| A reaction mechanism for iodoalkane from an alkane |
Thus, formed
iodine
increases the rate of forwarding reaction. Hence the iodination of alkane must be carried out in presence of a strong oxidizing agent.
 |
| The reaction of formation of iodomethane from methane in presence of conc.HNO3 |
2. From alkenes(Hydrohalogenation of alkenes)
The haloalkanes are prepared by the reaction of an alkene with halogen acid (HF, HCl, HBr, HI). The reaction is called the Hydrohalogenation reaction.
chloroethane
If an unsymmetrical alkene is taken then two possible
products are formed.
CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
1-chloropropane
The Formation and stability of these two products can be explained by following two rules:
[A] Markovnikov’s rule:
According to this rule “when an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with an unsymmetrical reagent than the positive
part of reagent goes to that double bonded carbon
containing greater number of the hydrogen atoms”. For example
[B] Peroxide effect (Anti- Markovnikov’s rule)
According to this rule “when an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with the unsymmetrical reagent in presence of
organic peroxide
(R-O-O-R)then the positive part of the reagent goes to that double bonded carbon containing less number of
the hydrogen atom”. For example,
 |
| Anti-Markovnikov’s reaction |
It is also called the Kharasch effect.
HCl and HI do not give Markovnikov’s addition, why?
Ans: H-Cl is highly polar and hence does not undergo hemolysis
easily. HI undergoes homolysis to give iodine free radicals
which instantly combine to give I2.
3. From Alcohol
Generally, haloalkanes are prepared by the reaction of alcohols with haloacids or phosphorous halide, or thionyl chloride.
(a) Reaction with halogen acid(HX)
The
chloroalkane
is prepared by the reaction of alcohol with HCl in presence of anhydrous
zinc chloride (ZnCl₂).
The mixture of conc. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl₂ is called Lucas
reagent.
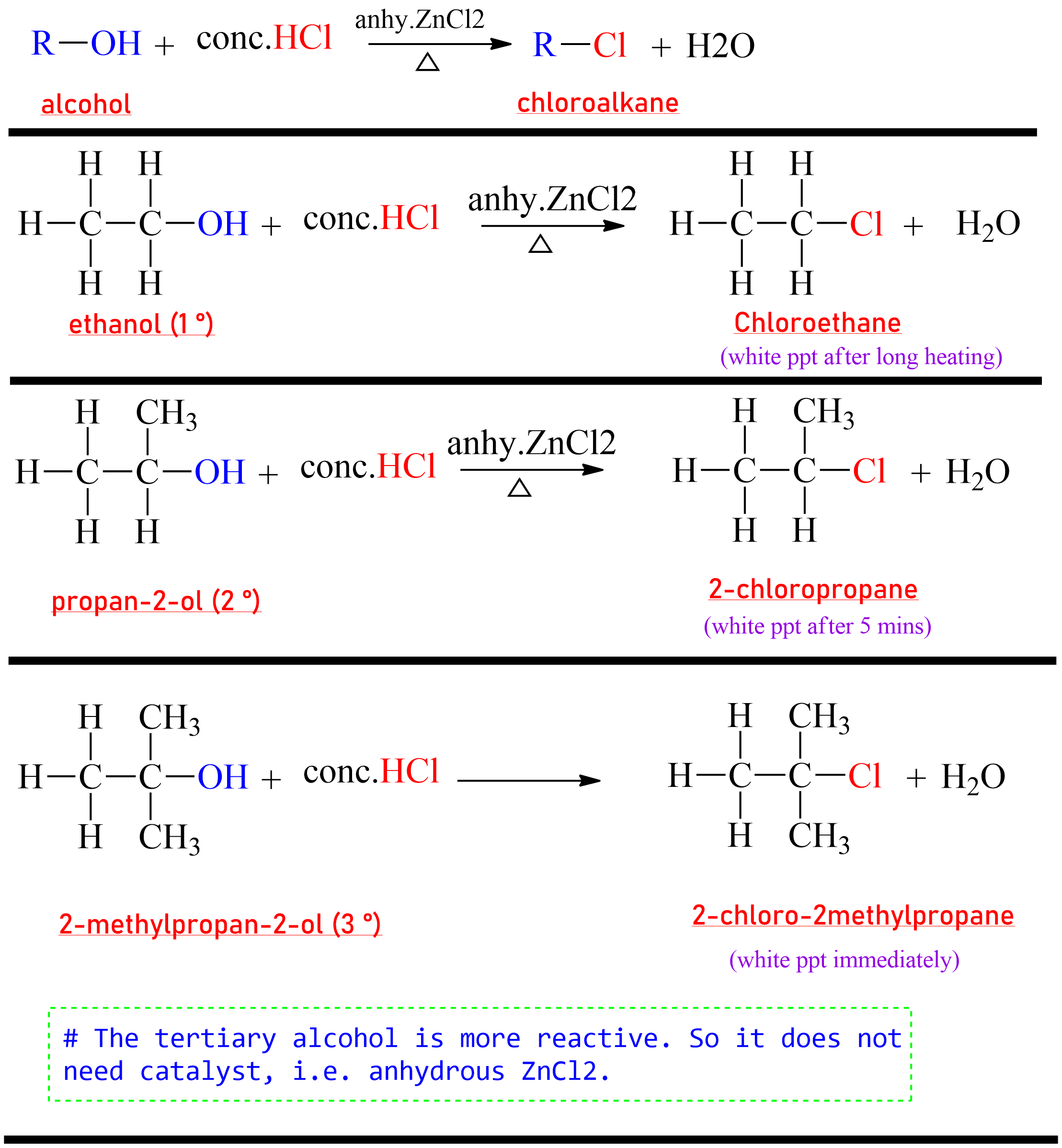 |
| A reaction from 1,2,3 degree alcohol to respective Chloro substituted product. |
HI> HBr > HCl
(b) Reaction with a phosphorous halide (PX₅ or PX₃)
The haloalkanes are prepared by the action of
alcohol with PX₅ or PX₃.
Chloroethne+phosphoryl chloride
phosphorous acid
Since PBr₃ and PI₃ are unstable compounds. So they are prepared in the reaction mixture (In-situ form)
by the action of red phosphorous with Br₂ or I₂.
bromoethane
iodoethane
The chloroalkanes are prepared by heating alcohol with SOCl₂ in presence of pyridine. Only chloroalkane is prepared
by this method. From this method, pure chloroalkane can be
prepared because SO₂ and HCl evolved as gases.
 |
| Darzen’s Reaction or Reaction of alcohol with thionyl chloride.
|
Physical properties of haloalkanes
- Lower members of haloalkane methyl chloride and methyl bromide are
colorless gases, higher are colorless and sweet-smelling liquids and
next higher are colorless solids.
- They are insoluble in water and soluble in almost all organic
solvents like ether, alcohol, etc.
- They burn with green-edged flame in the air.
- The boiling point of haloalkanes is higher than corresponding
parent alkanes.
- The boiling point of haloalkane having the same alkyl group is
RI>RBr > RCl due to the large size of the halogen atom.
- Branched-chain haloalkane has a lower boiling point than
straight-chain haloalkane due to its spherical nature.
- The B.P. increase as the increase in the alkyl group.
Chemical properties of haloalkanes
The haloalkanes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of polar C-X bonds. The polarity arises due to the difference in electronegativity
value between carbon and a halogen atom.
[A] Nucleophilic substitution reaction
The nucleophile is electron-rich species having lone pairs of electrons or negative charges and can attack
to electron-deficient center. When a
nucleophile
is substituted by another nucleophile then the reaction is called a
nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Nuc: + R-LG → R-Nuc + LG:
Nuc– nucleophile LG– Leaving group
Example: R-Br + OH− → R-OH + Br−
Here, the existing nucleophile has been substituted by an
incoming nucleophile.
The alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN- reaction ) by following two mechanisms.
S stands for Substitution
N stand for Nucleophile
The number represents Kinetic order
SN1 reaction:
represented as SN1.
Alkyl halide ionizes to give carbocation. Then step is slow and hence it is the rate-determining step.
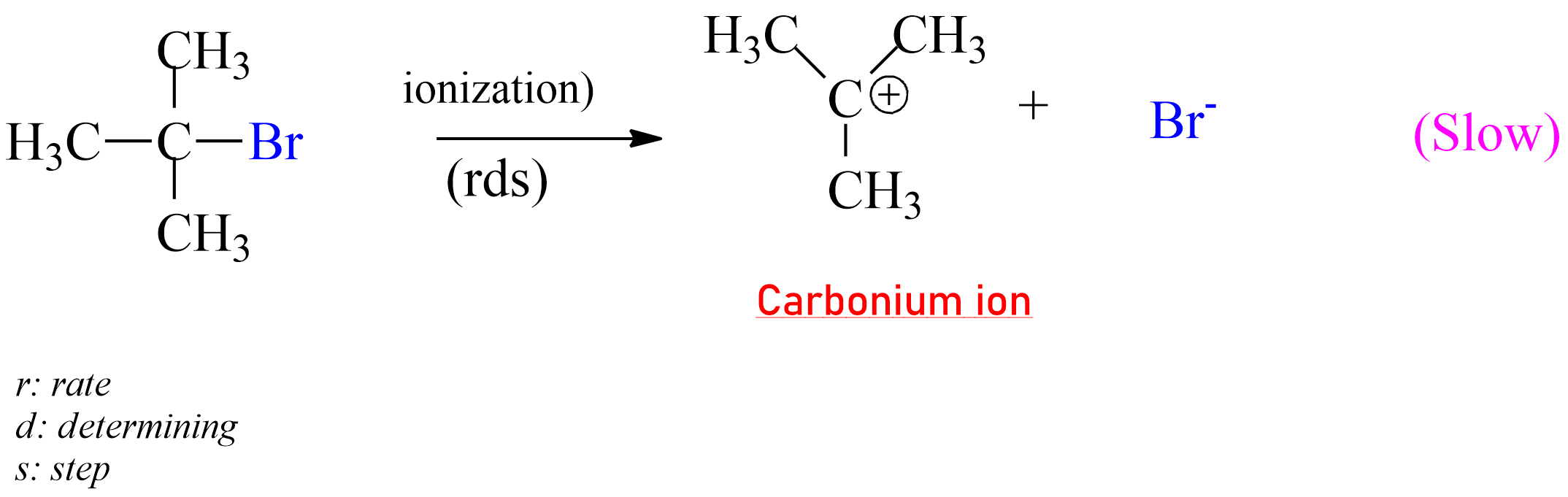 |
| The rate-determining step of SN1 Reaction |
In the second step, the nucleophile attacks the carbonium ion to give t-butyl
alcohol. (ionic reaction, fast)
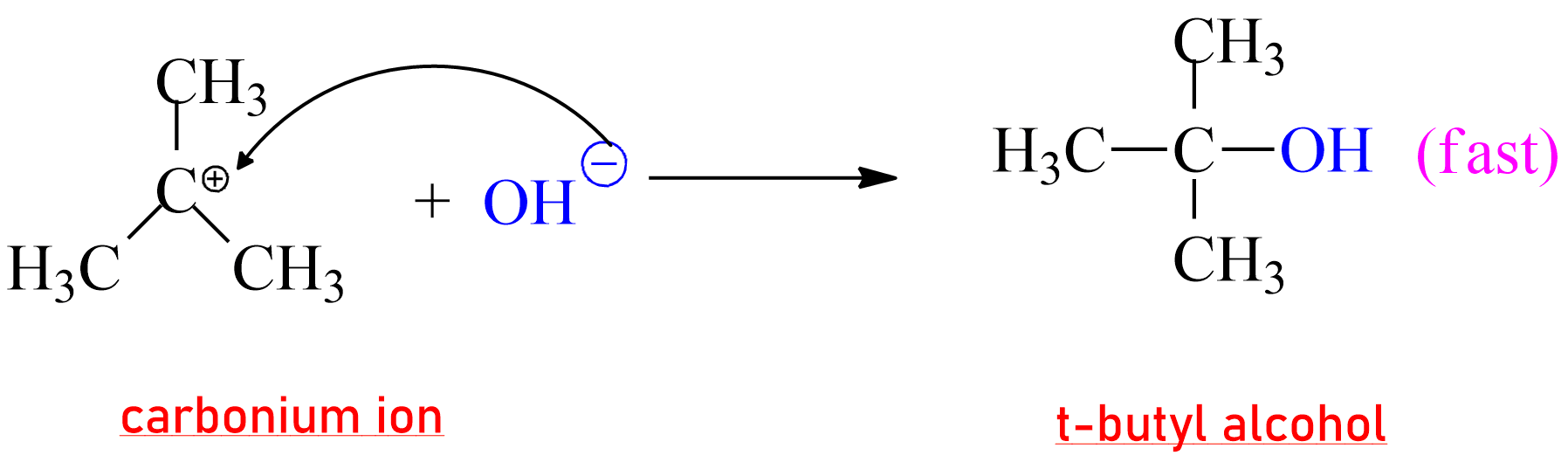 |
| Formation of product in SN1 Reaction |
SN2 reaction:

Difference Between SN1 and SN2 Reaction
| SN1 | SN2 |
| This follows the Unimolecular Rate of Reaction mechanism | This follows the Bimolecular Rate of Reaction mechanism |
| Follows 1st order Kinetic Reaction | Follows 2nd order Kinetic Reaction |
| Two-Step Mechanism | One Step Mechanism |
| A carbocation is formed as an intermediate part | No Carbocation |
| Racemization occurs | Inversion occurs |
| Order: 3°>2°>1° | Order: 1°>2°>3° |
| RoR∝ [ substituent] | RoR∝ [ substituent].[ Nucleophile] |
When
haloalkane
reacts
with an aqueous
solution
of
NaOH or KOH
then
alcohol
is
formed.
Ambident Nucleophile
Those nucleophiles that consist of possible two attacking sites on the
electron-deficient center are called ambident nucleophiles. For example,
NO₂⁻, CN⁻, etc. Cyanide ion is an ambident nucleophile because both
carbon and nitrogen can supply a pair of electrons during the
nucleophilic attack.
⟶
Similarly, NO₂⁻has two attacking sites.
–NO₂ & –ONO
R-X+CN⁻ ⟶ R-CN (Attack by carbon)
R-X+CN⁻ ⟶ R-NC (Attack by nitrogen)
2.
Reaction with alcoholic NaCN or
KCN
When haloalkane is heated with an alcoholic solution of NaCN or KCN
then alkane nitrile (Cyanides) are formed. This reaction is largely
used to increase the number of carbon atoms during organic
conversion.
carbon atoms)
Alkane nitrile(Cyanides) is a beneficial chemical that gives
various products when treated with different reagents.
(a) Reduction Reaction
A reaction in which an organic nitrile is reduced by nascent
hydrogen (e.g. from sodium in ethanol) to a primary
amine is REDUCTION REACTION.
b) Complete hydrolysis
NH₄Cl
ethanoic acid
c) partial hydrolysis
Q. Convert methane to ethanoic acid
3.
Reaction
with
alcoholic AgCN
When haloalkane is heated with an alcoholic solution of AgCN then
alkyl isocyanide is formed.
Here, AgCN is a covalent compound. So it does not dissociate
easily. Therefore the lone pair of electrons in the nitrogen
atom attacks haloalkane to form isocyanides.
Similarly, isocyanide forms different compounds as:
(a)Reduction
(b)Acidic hydrolysis
4. Formation of amines
When haloalkane is heated with alc. ammonia then amines are
formed.
Amine
5. Reaction with sodium alkoxide(R-ONa) (Williamson’s ether
synthesis/ Formation of ether)
When haloalkane is heated with
sodium alkoxide
then ether is formed. This reaction is called Williamson’s
etherification reaction.
½H₂↑
Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ether can be prepared
by this method.
6. Formation of thioether
Thioether is (R–S–R”) analog of ether.
Name sulfides like ethers, replacing ”sulfide” for “ether” in the
common name, or “alkylthio” for “alkoxy” in the IUPAC system.
7. Carbylanime
When primary animes are heated with alcoholic
potassium hydroxide
(KOH) and chloroform forms a product which is a foul-smelling substance called carbylanime
reaction.
+ CHCl3 + 3KOH → RNC (Carbylamine) + 3KCl + 3H2O
8. Reaction with aqueous NaNO₂ or KNO₂
When haloalkanes are heated with aqueous NaNO₂ or KNO₂ solution
then alkyl nitrite is formed.
Here, NaNO₂ is an ionic compound. Hence Na−O bond breaks easily and
negatively charged oxygen attacks haloalkane to form alkyl
nitrite.[Na-O-N=O]→[Na⁺+ ONO⁻]
9. Reaction with alcoholic silver nitrite (AgNO₂)
When haloalkanes are heated with alcoholic AgNO₂ solution then
nitroalkanes are formed.
nitromethane
Here, AgNO₂ is a
covalent compound. Hence the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom attacks an
alkyl group of haloalkane to form
nitroalkane.[Ag-O-N=O]→[Ag−NO₂]
[B] Elimination reaction (ᵦ- elimination reaction)
Dehydrohalogenation reaction
When haloalkane is boiled with an alcoholic solution of NaOH or KOH
then alkene is formed. In this reaction, one hydrogen and halogen
atom are removed from adjacent carbon. So this reaction is called
dehydrohalogenation reaction.
This reaction is also called β-elimination or
1,2-elimination.
Saytzeff’s rule
If
dehydrohalogenation
of haloalkane gives two or more alkenes then alkene containing a
greater number of the alkyl group on double bonded carbon is the
major product. This rule is called Saytzeff ’s rule.
 |
| Saytzeff’s rule |
Q. Convert 1-bromopropane to 2-bromopropane.
[C] Reaction with metal
Reaction with sodium (Wurtz’s reaction)
When alkyl halide is heated with sodium metal in presence of
dry ether, then alkane having a double number of carbon atoms is formed.
Therefore it is used to increase carbon length.
 |
| Reaction with sodium ( Wurtz’s reaction ) |
[D] Reduction reaction of Haloalkane
1. Catalytic reduction
2. Reduction with metal hydride
Ethane
3. Reduction with metallic solution
- Sn-Zn-Fe/HCl
- C₂H₅OH/Na
- Red.P₄/HI
Preparation of Chloroform
The chloroform is prepared in the lab by heating ethanol or
acetone
with the aqueous paste of
bleaching powder. In this process, the bleaching powder acts as an oxidizing agent,
chlorinating agent as well as the hydrolyzing agent.
1. From ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
(a) Oxidation of ethanol:
Chlorine oxidizes ethanol into ethanal.
(b) Chlorination of ethanal:
Excess chlorine reacts with ethanal to give chloral.
(c) Hydrolysis of chloral:
The chloral is hydrolyzed with Ca(OH)₂ to form
chloroform.
2. From propanone (acetone)
(a) Chlorination of acetone
Acetone is chlorinated by passing excess chlorine through forming tri
chloroacetone.
(b) Hydrolysis of tri chloroacetone
At last, tri chloroacetone is hydrolyzed with calcium hydroxide to
form chloroform.
Physical properties of Chloroform
- It is a colorless mobile oily liquid.
- Its boiling point is 61 ̊C and melting point is -60 ̊C.
- It is heavier than water having an sp. gravity of 1.48.
- It has a characteristic sweet smell and taste.
- It is insoluble in water and soluble in almost all organic
- solvents like benzene, ether, etc.
- It is a good solvent for dissolving fats, oils, resins, waxes,
etc.
- The Vapour of chloroform causes temporary unconsciousness when
taken in small amounts. So, it is used as an anesthetic drug. *Why it happen?
Chemical properties of chloroform
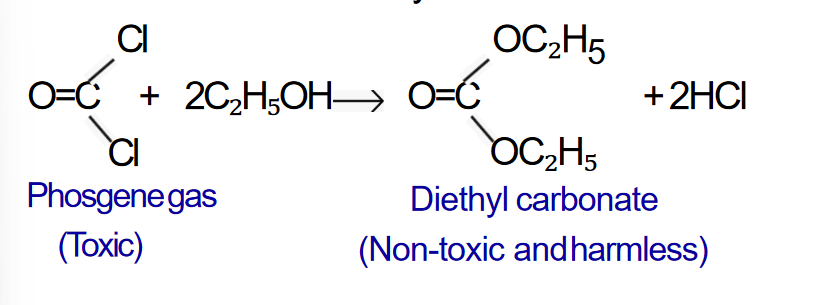
1. Action with air (Oxidation)
When chloroform is exposed to air in presence of sunlight, a
highly poisonous
phosgene gas (Carbonyl chloride) is formed.
Therefore, the following precautions are taken while storing the
chloroform.
- It is always stored in a dark brown colored bottle to protect it
from sunlight.
- It is completely filled up in the bottle to keep out air.
- A small amount (1%) of ethyl alcohol is added to the bottle of
chloroform. The ethyl alcohol reacts with phosgene gas formed
during storage to give non-toxic harmless diethyl carbonate.
2. Reaction with silver powder
When chloroform is heated with silver powder then acetylene is
formed.
3. Reaction with conc.HNO₃(Nitration)
When chloroform is treated with conc. nitric acid then chloropicrin is formed which is used as an insecticide and war gas (Tear gas).
4. Reaction with acetone
When chloroform is the heated presence of aqueous NaOH or KOH
then with acetone in a crystalline solid of chloretone is formed
which is used
hypnotic drug
(sleep-inducing).
5. Reduction
i)Acidic medium(Zn/HCl)
When chloroform is reduced in an acidic medium, methylene chloride
is formed.
ii)Basic medium(Zn/H₂O)
On reduction in neutral medium, methane is formed.
Purity test of chloroform
6. Reaction with silver nitrate (AgNO₃)
i) With Pure Chloroform
Pure chloroform does not give white ppt. with AgNO₃ solution
because the C-Cl bond in chloroform is a strong covalent bond and
can not give Cl⁻ ion.
ii) With impure Chloroform
But, impure chloroform gives white ppt. of AgCl with AgNO₃ due to
the presence of Cl⁻ ion after the
oxidation
of chloroform in the air.
HCl+AgNO₃ ⟶ AgCl↓ +HNO₃
(white ppt)


Read More: Class 12 Chemistry
Important Question For
Haloalkane and Chloroform
 |
| Fig: Haloalkanes whole syllabus/course content |
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by haloalkanes?
Haloalkanes and haloarenes are hydrocarbons in which one or
more hydrogen atoms have been replaced with halogen atoms.
What haloalkanes called?
The haloalkanes, also known as alkyl halides, are a group of
chemical compounds comprised of an alkane with one or more
hydrogens replaced by a halogen atom (fluorine, chlorine,
bromine, or iodine).
What are haloalkanes with examples?
The haloalkanes are a group of chemical compounds comprised
of an alkane with one or more hydrogens replaced by a
halogen atom (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine).
Example: Chloroethane (CH3CH2Cl).
What are the uses of haloalkanes and Haloarenes?
Haloalkanes and haloarenes are used for many industrial and
day to day purposes. They are used as flame retardants,
propellants, solvents, pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, fire
extinguishants, and many more. They are used as solvents for
non-polar compounds.
How many types of haloalkanes are there?
Halogenoalkanes are also called haloalkanes or alkyl
halides. All halogenoalkanes contain a halogen atom –
fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine – attached to an alkyl
group. There are three different kinds of halogenoalkanes:
Primary, secondary and tertiary.
Why haloalkanes are more reactive than Haloarenes?
Greater the dipole moment, greater is the polarity and more
is the reactivity. Thus, C−X bond of haloalkane is more
polar than the C−X bond of haloarene. Hence, haloarenes are
less reactive than haloalkanes.
What is the difference between haloalkanes and Haloarenes?
When hydrogen atoms in aliphatic hydrocarbons(alkanes) are
replaced by halogen atoms ,the compounds formed are known as
haloalkanes. Similarly, when hydrogen atoms attached to
benzene rings are replaced by halogen atoms the compounds
that are formed are known as haloarenes.
What is the haloalkanes formula?
CnH2n+2=Alkanes, CnH2n−2=Alkynes, CnH2n=Alkene, and CnH2n+1X
is haloalkanes.


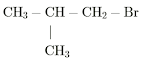



![NEB Class 12 Exam Routine 2082 [2025] 2 NEB Class 12 Exam Routine 2081/2082 [2025]](https://iswori.com.np/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/neb-class-12-routine.png)